Hemp and Sustainability – 51 Things About This Super Plant Saving Our Planet
By the first quarter of the 21st century, the struggle to implement sustainable measures has become more difficult than ever before.
In 2020, humans had already overused 75% of the planet’s resources. This meant that the rate of consumption was equivalent to 1.75 Earths that could sustain it. In the search for sustainable options, adopting hemp can bring about a radical change. Hemp’s diverse nature and flexibility in its use across different sectors can make it the most preferred sustainable solution in the coming years.
We’ll see how hemp and sustainability coexist in promising ways. Let’s explore 51 things about hemp’s role in sustainability
Hemp Facts In Sustainable Agriculture
1. Deep taproot systems act as nature’s rebar
Hemp grows a deep and complex taproot system that binds the soil and improves soil aeration, water seepage, and nutrient absorption. Depending on soil conditions, hemp roots can grow 10-12 inches in a month. On average, its secondary roots can grow up to 2.5 feet, while the primary root can be 6-8 feet deep.
2. Year-round soil protection
Post-harvest, hemp stalks and roots that are left behind protect the soil. Quick decay of these remains acts as a natural mulch, adding back organic matter to the soil. This provides excellent soil protection, especially in winter when the soil remains exposed. Hemp can return two-thirds of organic matter if it is field-retted.
3. Excellent rotation crop
Several studies show excellent results of crop rotation in the use of hemp and sustainability in agriculture. Crops like corn, soybeans, tobacco, and wheat grown in rotation with hemp have shown a 10-20% increase in yields in subsequent yields. A study in China that researched hemp facts as a rotational crop found that diseases decreased, plant yields increased, and soil microbial diversity enhanced.
4. Strong phytoremediation properties
Hemp acts like a natural vacuum cleaner for contaminated soils. Heavy metals like cadmium, lead, copper, and nickel are removed by the crop. With its deeply penetrating root system, it provides heavy metal extraction from deep soil-level accumulations. During the growing season, hemp can remove up to 50% of cadmium and 90% of lead from polluted soil. Studies on the role of hemp in removing soil contaminants have shown positive results in hemp statistics. Hemp can reduce exchangeable cesium in the soil by 11%–23%.
5. Natural weed suppressor
Hemp is a fast-growing crop, and in its growth stage, it forms a canopy with dense foliage. The shade suppresses weeds and prevents the need for chemical herbicides. Studies show that hemp can significantly reduce the most resilient weeds, like bindweed and knapweed, within a season.
6. Carbon sequestration
Hemp can absorb more CO2 per acre than trees. It captures atmospheric carbon at double the rate of forests. It stores approximately 45% of the atmospheric carbon taken up during photosynthesis. Hemp’s ability as an excellent carbon sink is shown in hemp and sustainability in land management.
7. Water efficiency and conservation
Hemp is a highly sustainable fiber crop due to its modest water requirements. Cotton, a popular eco-friendly choice for natural fiber, needs 10,000 liters of water to produce 1 kg of fiber. Hemp often grows using only natural rainwater and without irrigation. It has a 38% lower crop water requirement and a 60% lower water footprint compared to cotton. It requires 84% lower crop irrigation and has a 91% lower irrigated water footprint than cotton. Adding to these remarkable hemp statistics about water efficiency is the fact that it is a highly drought-resistant crop.
8. Hemp promotes biodiversity
As a rotational crop, hemp can maintain a flourishing biodiversity for years. The dense foliage and canopies developed by the closely growing plants can create mini ecosystems and link fragmented and fragile habitats. Hemp produces a high volume of pollen when other crops aren’t. This helps pollinators like bees thrive in late seasons.
9. High pest resistance reduces reliance on chemical pesticides
Hemp has natural resistance to a lot of pests and diseases. This makes it an attractive natural fiber crop. Hemp is used as a part of integrated pest management systems (IPM) where physical, biological, and chemical strategies are combined with resistant host plants. As intensive pesticide use is not needed for hemp, it benefits fauna such as bees and butterflies.
10. Less reliance on chemical fertilizers
One of the important hemp facts in sustainable agriculture is the reduced need for nitrogen fertilizers in hemp cultivation. This tackles an important environmental issue with fertilizers that make the soil acidic by leaching nitrates. Hemp’s deep root system easily absorbs mineralized nitrogen available in the soil. When hemp is used with legumes as cover crops, it further enriches the soil and significantly reduces the need for adding nitrogen fertilizers.
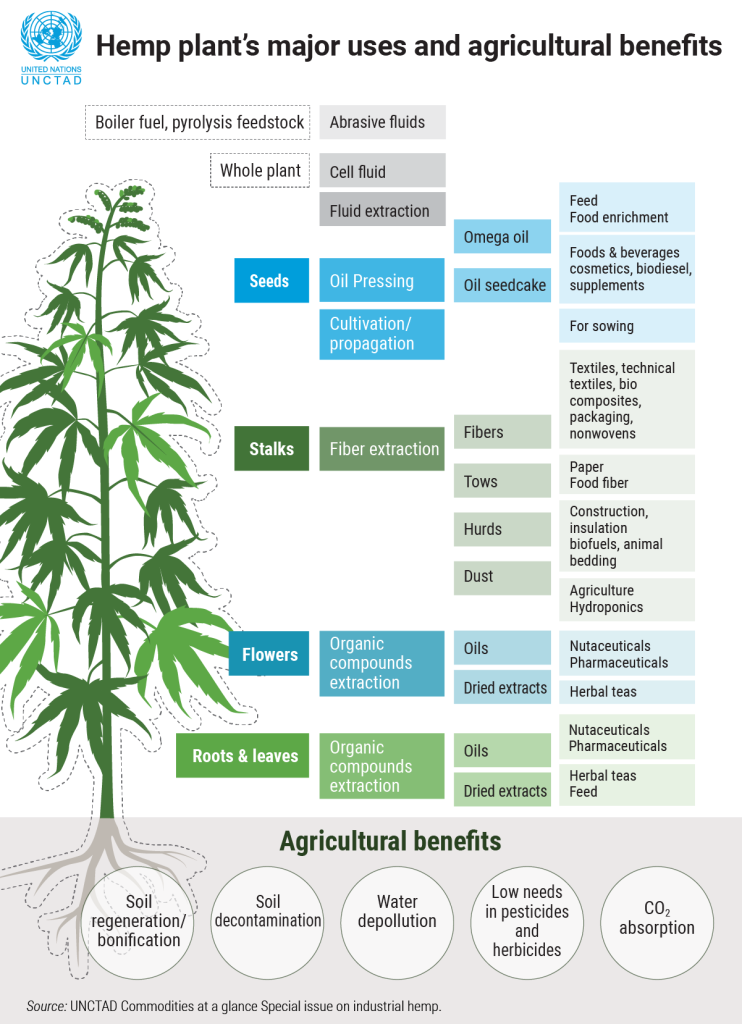
Hemp And Sustainability In Construction
11. Hempcrete as a sustainable building material
Hempcrete in construction and buildings can bring a sustainable shift to industrial practices. Hempcrete is made from hemp hurds, lime, and water. It is sourced from sustainable materials, and at the end of a building’s life, it can be composted and used as a soil additive. Made from natural and sustainable materials, hempcrete has lower embodied energy than cement.
12. Use of hemp oil as a non-toxic natural sealant
Hemp oil can be polymerized for a variety of finishes. Hemp oil is a drying oil offering deep penetration, enhancing natural wood, and creating a waterproof barrier. Speaking of hemp and sustainability, using hemp oil in sealants and paints doesn’t release VOCs or hazardous pollutants, unlike chemical sealants.
13. Sustainable flooring
Hemp flooring is done using hemp as engineered wood. Hemp can be the only component or a composite material. It can be used as a replacement for traditional wooden floors. Hemp wood is harder than oak. It can reach up to 2,750 on the Janka Hardness scale. It is resistant to damage and scratches and can be refinished like hardwood. This can reduce pressure on forestlands and combat deforestation.
14. UV resistance of hemp-based decking
One of the interesting hemp uses relevant in sustainable construction is hemp-based composite decking. It is made from hemp fibers and thermoplastics, exhibiting high durability and weather resistance. It is used in outdoor or exposed constructions like verandas, terraces, and garden structures. The presence of natural pigments and lignin in hemp gives it high resistance against UV rays. Its high UV resistance makes it last longer than traditional wooden decking.
15. Sustainable alternative to synthetic materials in acoustic insulation
Hemp’s fibrous nature and uneven particle surface makes it a poor sound transmitter. Hemp has 78% porosity with pores between 0.9-3 μm. Using hemp in composites enhances acoustic insulation properties. Compared to cotton fiber-reinforced composites, hemp fiber composites demonstrate significantly higher sound insulation at high frequencies. Hemp wool’s properties in sound absorption are much superior to fiberglass and are as good as cellulose fiber. Hemp acoustic panels are excellent for absorbing low sound frequencies, which is a challenge for many traditional insulators.
In continuation to hemp and sustainability in construction, let’s take a look at some more interesting hemp facts and hemp statistics in brief:
16. Carbon sequestration in hempcrete: As a carbon-negative material, it is more effective than zero-carbon materials. Apart from carbon sequestering while hemp grows, once converted to hempcrete, carbon absorption continues till 100 years. Hempcrete captures around 110 kg of CO2 per cubic meter of wall.
17. Thermal resistance in hemp-based materials: Usage of hempcrete can treat urban heat island issues and reduce emissions. It performs better than fiberglass and mineral wool in heat regulation. Unlike fiberglass they don’t irritate skin or lungs during installation.
18. Breathing wall effect: Hemp walls absorb moisture when humidity is high and release stored moisture when the air is dry. It can absorb 20% of its weight in moisture without losing its structural integrity or insulating properties. This makes it perfect for use in restoration and upgrade in historical buildings.
19. Mold resistance: Hempcrete has a high pH level. This, along with its breathability and hygroscopic properties, retards the growth of mold, mildew, fungi, and mites.
20. Non toxic: Hemp-based materials don’t have toxic emissions during use or end-of-life demolition. They are also free from VOCs like formaldehyde, commonly found in traditional construction materials.
21. Enhances indoor air quality: Thermal insulation, moisture regulation, and mold prevention of hemp walls ensure improved air quality. It reduces the need for mechanical air ventilation systems.
22. Drywall alternative: Hemp panels are stronger and more sustainable than traditional drywalls. Their finish is similar to conventional drywalls while providing better thermal mass and moisture regulation.
23. Structural reinforcements: Hemp fibers can be used in creating lightweight reinforcements for concrete and other building materials. Their strength is similar to steel reinforcements. They are specifically useful in anti-corrosion and rust-free applications.

Hemp And Sustainability In Textiles And Fashion
24. Low Environmental impact of hemp fiber textile
As an eco-friendly fiber, it has lower environmental costs than cotton. Compared to cotton, hemp uses less water, gives a higher yield producing more fibers per acre, and requires less land for cultivation. Hemp is a sustainable alternative to natural fibers like cotton and synthetics like polyester.
25. Degrades faster than cotton
As a natural fiber, one of the obvious hemp facts is that it is completely biodegradable. It decomposes way faster than cotton, making it the next revolutionary fabric in the textile industry. In comparison, hemp can biodegrade in two weeks while cotton can take 5 months. In landfills, hemp fibers can naturally compost in 6-12 months, while synthetic fibers take hundreds of years.
26. Long-lasting fabric durability
Studies show that hemp can be 3-8 times stronger than other natural fabrics. It has double the textile strength of cotton fabric. Hemp fibers have high abrasion resistance and tensile strength, which gives them better structural integrity than other natural fibers. The fabric strengthens with use and multiple washes, making it perfect for heavy-duty workwear and industrial clothing.
27. UV-resistant textile applications
Hemp fabric often has a UPF rating of 40 or more. Depending on the weave, it can have an SPF of 15-50. Hemp statistics show some hemp fabrics can block 99.9% of harmful UVA and UVB rays. It doesn’t require chemical treatment to make it UV-proof. As it doesn’t fade or disintegrate in sunlight, it is even better than synthetic textiles for use in protective gear.
Some more interesting hemp facts and hemp statistics on the sustainable use of hemp in textiles:
28. Antimicrobial property: Hemp’s natural anti-microbial properties makes it a good choice in versatile textile applications. It inhibits the growth of fungus and bacteria, keeping the fabric odor-free. This makes it useful in medical textiles, intimate wear, and sportswear.
29. Denim alternative: Hemp fibers are perfect for jeans because of their durability and eco-friendliness. It is more breathable than cotton denim. It also uses less water and chemicals in denim production than cotton denim.
30. Eco-friendly blends: Luxurious eco-friendly blends are made using hemp and silk. For softer fabrics and moisture-wicking properties hemp and cotton blends are used.
31. Use in natural fiber home furnishings: The durability and sturdiness of hemp textiles find application in upholstery and drapery. They age well, and the natural fiber variations can create beautiful texture options for interior decoration.

Renewable Energy And Biofuel Options With Hemp
32. High biomass yield for biofuel
The entire plant can be used for energy production, including its by-products like shives and straws. In tackling the fossil fuel and deforestation problems, measures in hemp and sustainability in energy production can bring a huge transformation. One acre of hemp can produce four times the biomass as an acre of trees. It becomes ready for harvest in months rather than years. Hemp biomass has a calorific value of 17,100 kJ·kg⁻¹, which is comparable to other energy crops.
33. High energy yield
Hemp produces more energy per acre than most other biofuel crops. In biogas production, the adjusted biomass energy yield of hemp is similar to that of maize and sugar beet. Hemp statistics show that hemp’s energy yield is 24% more than that of lucerne and 14% more than that of clover-grass ley. It was found that the energy efficiency per hectare of hemp under water shortage was 10% higher than that of maize under the same conditions.
34. Production of biodiesel
Hemp seeds contain 30-35% oil that can be easily converted to biodiesel. In a year, hemp can produce more than 800 liters of biodiesel per hectare. This surpasses other energy crops like soybean, sunflower, peanut, and rapeseed. After production of the biodiesel, the discarded stems can be used as raw materials for other uses. The biodiesel is suitable as high-grade diesel fuel oil and airplane engine and precision machine oil.
35. Production of Bioethanol
Hemp’s high cellulose content makes it an excellent source for ethanol production. Hemp produces more ethanol per acre than corn. It requires fewer inputs and can be grown on marginal land. A plant consuming 85 tons of hemp biomass an hour can produce 114 kilotons of ethanol per year. When using the entire hemp plant, it is more efficient than corn-based ethanol production. Utilizing the entire hemp plant can produce 3000 liters of ethanol when co-produced with methane.
36. Lower carbon emissions
One of the top hemp facts is that it is carbon-neutral as a biofuel. The CO2 released during biofuel combustion is equivalent to that absorbed by the hemp plant during its growth. This is a practical solution to mitigate GHG. As the crop sequesters significant amounts of CO2, it offsets the emissions generated during biofuel production. The cultivation of hemp acts as a carbon sink. When hemp is processed into biofuels, it maintains a closed carbon cycle.
37. Absence of sulfur makes it a clean fuel
SOx compounds released from fossil fuels are a major environmental concern in fuel combustion. It causes acid rain, and the sulfur leaching into soils makes it acidic. Hemp biodiesel is a cleaner alternative with no sulfur emissions. The biomass conversion into fuels also doesn’t emit sulfur.
A few more hemp facts in energy and biofuel:
38. Biochar: Hemp can bio-sequester and return CO2 back to the soil as biochar. It is a renewable alternative to charcoal. The high-quality hemp biochar improves soil quality.
39. Local energy source: Hemp’s adaptability to a variety of climates makes it a sustainable source of local energy production. It reduces costs of import, transportation, and dependency on centralized energy sources. It can create local jobs and empower the local economy.
40. Agricultural waste recovery: High cellulose percentage in hemp makes it efficient for cellulose extraction from agricultural waste. The maximum cellulose content in hemp can be three times that of wood. After harvesting the crop, the remaining parts can be converted to energy on-site on the farm to create a closed-loop system.

Let’s wrap up the list on hemp and sustainability and hemp statistics on its sustainable use with a few more interesting hemp facts in the consumer category:
41. Natural skin ingredient: Hemp seed oil is gentle and natural, rich in omega fatty acids and non-comedogenic. Hemp statistics of the oil’s properties in skin hydration in a study showed that soap containing 1% of hemp seed oil dramatically increased skin hydration between 15-30 minutes.
42. Bioplastics: With a 60-70% cellulose content, hemp poses as a strong contender to common plastic. Hemp plastic needs 22-45% less energy than non-renewable energy sources in production.
43. Hemp paper: It is more sustainable than wood pulp. Hemp gives four times more usable fiber than trees and matures faster. With a lower lignin content than wood, it doesn’t need chemical bleaching.
44. Biodegradable packaging: Hemp is stronger than paper, resistant to mold, and resistant to moisture. It can completely break down in industrial facilities in 60-90 days. These hemp facts make it a better choice than paper packaging.
45. Sustainable food products: Hemp seeds, oil, and protein powders are nutrient-rich and can offset the environmental impact of sourcing similar food sources.
46. Green cleaning products: Hemp-based cleaning products are safe, gentle, and don’t leave toxic residue. It is antimicrobial and biodegradable, making it an excellent cleanser for a wide range of uses, from personal care to industrial cleaning.
47. Ecofriendly industrial lubricants: Hemp oil is a high-performing lubricant. It is non-toxic and biodegradable with a great potential to replace petroleum lubricants.
48. Pet care: Hemp can be used in pet bedding, grooming products, and accessories. It controls odor and is durable for heavy use.
49. Hemp milk: Hemp is a complete protein source containing all the nine essential amino acids. It is rich in omega fats along with other nutrients. This makes hemp milk a good dairy alternative for vegans and lactose intolerants.
50. Food storage: Food storage and packaging using hemp plastics is not only eco-friendly but also safe, as hemp doesn’t have toxic chemicals that can leach into the food.
51. Biodegradable disposables: Single-use items made from hemp are better than paper as they are more durable and free from toxins. It is definitely a sustainable choice over plastic disposables.
While concluding this exhaustive list of facts on hemp and sustainability, let’s shed light on the fact that hemp can be a part of an economic boom. Based on hemp statistics, the global hemp market is projected to reach $18.6 billion by 2027. Its versatility and sustainability are a huge opportunity in economic expansion while securing a sustainable future.
Vishal Vivek
Vishal Vivek is the Founder and CEO of Ukhi, a pioneering bio-materials company dedicated to ending plastic pollution by converting agricultural waste into high-performance compostable polymers. With a background in sustainable entrepreneurship and over a decade of technology experience, he leads Ukhi’s vision to create scalable, planet-positive material solutions. Previously, Vishal founded the Hemp Foundation, where he empowered more than 1,000 farmers and advanced sustainable livelihood initiatives. His work has been recognized through awards such as the HDFC Parivartan Grant and featured in leading publications like Forbes and Entrepreneur. Times Group recognized him as a legendary entrepreneur and published his biography in “I Did IT- Vol 2” alongside social pioneers like Bindeshwar Pathak (Sulabh International) and Anshu Gupta (Goonj). Vishal has authored more than 200 articles on sustainability and hemp, reflecting his deep expertise and advocacy for regenerative solutions. His commitment to grassroots impact led him to live in the remote mountains of Uttarakhand, where he immersed himself in the lives of marginal farmers, understanding their challenges and co-creating economic opportunities through hemp-based initiatives. A deeply passionate innovator, Vishal often draws inspiration from seemingly impossible achievements: “If Elon Musk can make rockets reusable, or Dashrath Manjhi can carve a path through a mountain with rudimentary tools, why can’t we eliminate the demon of single-use plastic while uplifting struggling farmers? We will make it happen—whatever it takes.” Ukhi is proud to be supported by premier institutions including IIT Guwahati, NSRCEL-IIM Bangalore, Indian School of Business (Hyderabad), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR Pusa), and the Indian Institute of Packaging. Vishal is committed to demonstrating that business can be a powerful catalyst for global environmental and social good. Connect with Vishal Vivek
Related Posts
How is Cotton Contributing to Climate Change?
Under the microscope: Green Houses Gases of the Cotton Industry Cotton is killing the climate.
Best Hemp Plastic Products to Buy Online (2026) in USA
There’s never been more noise in the world of hemp plastic products. Some are genuinely sustainabl




