Are Hemp Bioplastics Really Sustainable?
Hemp bioplastics are going to change the way we live. We analyze its sustainability.
The use of synthetic polymer is widespread, ranging from ubiquitous water bottles to aerospace manufacturing. DuPont™ Tedlar was used for Phoenix Mars Lander, DuPont™ Vespel is used to make satellites.

But plastic waste is a serious issue. Each year, about 8 million tons of plastic find their way to the oceans. Many tons of plastic are dumped into the ocean every minute.

In an era marked by rising climate consciousness, it is not acceptable.
Using hemp-based plastics is set to usher in a new era.
What are hemp-based plastics?
The hemp plant contains plenty of cellulose in the stem.
By processing, this can be easily converted to bioplastics.
What is the advantage? It is a plant product and not an oil-based one.
Whereas normal plastic takes many centuries to degrade, hemp plastics can decompose in a few months.
The idea is not new. As early as the 1940s Henry Ford, the legendary carmaker, had created a hemp bioplastic car.
In the past decade, hemp has made a strong comeback. Hemp clothing was the first to get our attention. It was followed by hemp seeds as a diet supplement. Now the world is seeing the transformative power of hemp plastic.
The big question is whether it has side effects or can prove to be harmful in any way.
What makes hemp plastics sustainable?
We analyze the reasons which make hemp bioplastics sustainable.
- Clean Manufacture
Traditionally, for the last eight decades, we have made plastic from petroleum. It is largely a byproduct of oil refining. That is why it is cheap and easily available.
The crude oil refining process is far from ideal. The refining industry is the third-largest producer of greenhouse gas (after transportation and coal-based power plants).

Compared to this mess, hemp plastic manufacturing is absolutely clean. All that is necessary is the extraction of cellulose from the dried stem.

This is achieved easily through age-old methods without harming the environment.
- Biodegradable
This is a huge plus point.
The landfills can’t take any more plastic. The oceans are suffering from a deluge of waste. The Great Pacific Garbage Patch covers 1.6 million sq km, an area roughly one-sixth the size of Europe.
Hemp plastic decomposes really quickly. In at most six months, a buried price of bioplastic would have completely changed to compost.
Essentially, it means we can reuse landfills. Either the compost is used for agricultural purposes or we use the land for housing, etc.
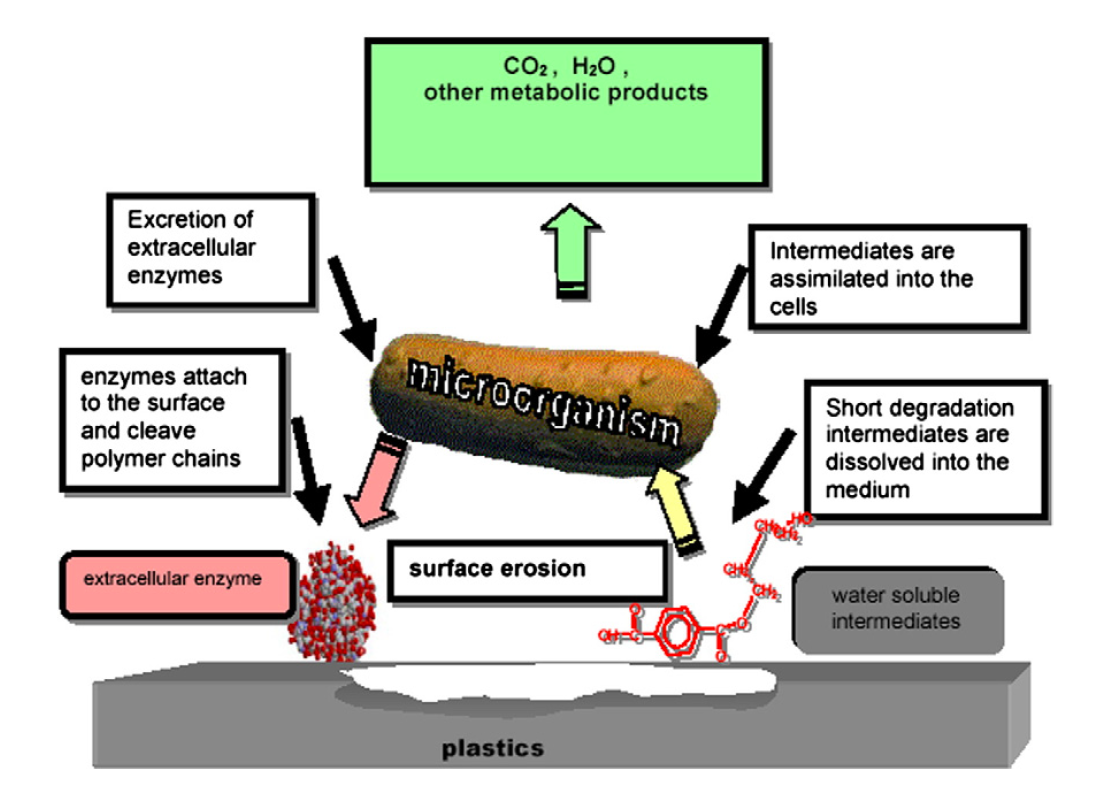
- Non-Poisonous
Toluene, benzene, and similar chemicals produced by refineries are carcinogenic. Constant association with them might cause cancer. This is a health risk that many workers in the oil industry are exposed to.
If ingested, these chemicals can cause death.
The use of hemp plastic provokes no such risk. After all, agriculture has been our occupation for thousands of years with no side effects.
Hemp farming is eco-friendly
This has equal importance. Hemp plastic originates from hemp stems. Unless the cultivation is clean and green, in no way can hemp bioplastic be termed sustainable.
- Grows on any soil
The hemp plant can grow on any type of soil except in frigid weather (North European) or desert (Middle East) conditions.
There are vast arid stretches in every country. Arizona, for example, is plagued by droughts. The farmers and local economy can benefit from a cash crop such as hemp that is easy to grow on any type of soil.
- Hemp has many uses
Hemp plastics are not the only product from the stem. Hemp textiles are in fashion. Hemp paper is on its way to the market.
This versatility is good news for farmers. They never have to worry if they will produce something that has a saturated market.
- Low reliance on pesticides
Pesticides sprayed indiscriminately are dangerous.
The dangerous chemicals seep into groundwater. They travel through the subsoil level to the nearest river and take the lethal concoctions downstream.
What can be more dangerous?
The hemp plant needs very little pesticides.

The strong smell drives them away.
Compare that to cotton which grows on 2.5% of the agrarian land surface but uses 16% of all pesticides.
- Needs less fertilizers
Plants use up a lot of nutrients from the soil. That is why the regular application of synthetic fertilizers is necessary.
What happens to it? Soaks into groundwater and ends up in our bodies.
Fertilizers are quite expensive and drive up the cost of production.

Hemp plants need a fraction of the fertilizer that other crops require. They have long taproots which penetrate several feet inside the soil.
Bringing up nutrients from deep underground does not deplete the topsoil.
- Prevents soil erosion
Hemp plants are tall, usually between 6 and 9 feet high. They grow close together like sugarcane.
The density of crop matters, since more can be produced per acre.
The other benefit is that the roots of so many plants tightly bind the soil. Even after harvest, the roots remain and protect the soil from being washed away.
- Grows quickly
Hemp grows fast. In as little as 5 months, the crop can be harvested.
It is easier to rotate between hemp and winter crops. Farmers can recoup their investment in as little as six months.
Moreover, every ton of hemp captures 1.6 tons of CO2 from the atmosphere. It cleans the air and the soil and is excellent for bioremediation.
Are there any downsides to Hemp Plastics?
Not really. The only potential problem is the lack of supply.
For too many years, farmers have thought of sugarcane and cotton as the only cash crops.
It is very recently that hemp has entered the picture. In fact, not even four years have elapsed since the cultivation was made legal in the US.
As more farmers come to know about how easily hemp can be cultivated, the supply bottleneck would ease greatly.
What does the future hold?
Hemp bioplastics are here to stay. Conventional plastic is on the way out.
Bioplastics are excellent for fabrication. They can be used perfectly in injection molds.
Many auto companies are actively investigating the role hemp plastics can play in future designs.
Hemp hurd is almost 80% cellulose and plastic made from it is perfect for cars. It is 3.5 times stronger than traditional plastics, and that matters for safety and durability.
That is good for publicity but expect wider adoption of hemp soon as businesses focus on making their product as environmentally friendly as possible.
Poly-lactic acid or PLA from hemp is being used by several industries, such as medical packaging. The next step is to replace single-use plastics like food packaging and bottles with suitable hemp bioplastics.
The emergence of hemp bioplastics is yet to make an impact due to supply constraints. That does not mean it is not making waves.
Sources
https://livepurepower.com/benefits-of-hemp-for-regeneratie-agriculture/
https://hashmuseum.com/en/cannabis-knowledge/industrial-hemp/hemp-based-plastic/
https://www.farmbusinessshow.co.uk/news/blog.asp?blog_id=21167
https://www.unsustainablemagazine.com/hemp-the-little-plant-that-could/
https://www.goodhemp.com/hemp-hub/environmental-benefits-of-hemp-how-good-is-it/
https://www.cannabistech.com/articles/hemp-plastics-a-look-at-the-pros-and-cons/
https://newfrontierdata.com/cannabis-insights/where-hemp-meets-the-road-automotive-bioplastics/




