7 Facts About Hemp’s Role in Cutting Carbon
In January 2025, the World Meteorological Organization confirmed what many of us had felt last year.
Namely, 2024 was the hottest year on record globally.
Not only that, but the past nine years have also been the warmest on record. The average global temperature has risen by a centigrade in the past century.
It can be allowed to rise by at most another half a degree before we face catastrophe.
The principal cause of global warming is increased CO2 levels in the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide levels are higher now than they have been in the past 2 million years. There is an urgent need to address the problem and reduce the amount of carbon dioxide.
Thankfully, in this crucial endeavor, we have a powerful ally –hemp.
Hemp, a sturdy annual plant, grows abundantly in the wild. It has been harvested for thousands of years, and there is archaeological evidence that it was used in China about 5,000 years ago. Hemp can help reduce carbon from the atmosphere.
Let us explore the extraordinary ways in which hemp reduces carbon dioxide levels.
7 facts about hemp and carbon reduction
Hemp is the perfect crop for reducing greenhouse gases and promoting sustainability.
Here are seven of the most compelling facts about hemp’s role in reducing carbon.
- Hemp is a Champion in CO2 Absorption
Plants absorb CO2 from the air during photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis combines carbon dioxide and water to make glycogen and cellulose.
While all plants capture carbon, hemp is a standout. Hemp and carbon reduction go hand-in-hand due to the plant’s efficient CO2 absorption.
This hardy crop can remove 15 tonnes of CO2 per hectare during its growth cycle.
The amount of carbon sequestration with hemp farming is amazing, indeed.
A medium-sized car emits around 4.6 metric tons of carbon dioxide each year, and a hectare of hemp can offset the emissions for over 3 years.
It is worthwhile to note that forests can only capture 2-6 tons of CO2 each year.
- Hemp Grows at Warp Speed
Not only does hemp absorb a lot of CO2, but it also grows incredibly fast.
It can shoot up to a height of 2 meters in just three months. The rapid growth of hemp makes it ideal for carbon reduction.
It can complete multiple carbon capture cycles within a single year.
Faster growth and plant maturity mean more crops each year.
The net effect is that more CO2 is absorbed in a shorter amount of time.
- Hemp is a Zero-Waste Crop
From its stalks to the seeds, every part of the hemp plant can be used.
Hemp bast fibers can be used to make pure hemp textiles or blended with other fibers like cotton or silk. Oil extracted from hemp seeds can moisturize skin, fight acne, and soothe conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
And that is not all. Hemp cellulose can be used to make bioplastics.
It is the perfect material for packaging and reduces our dependence on traditional plastic and the pollution it causes.
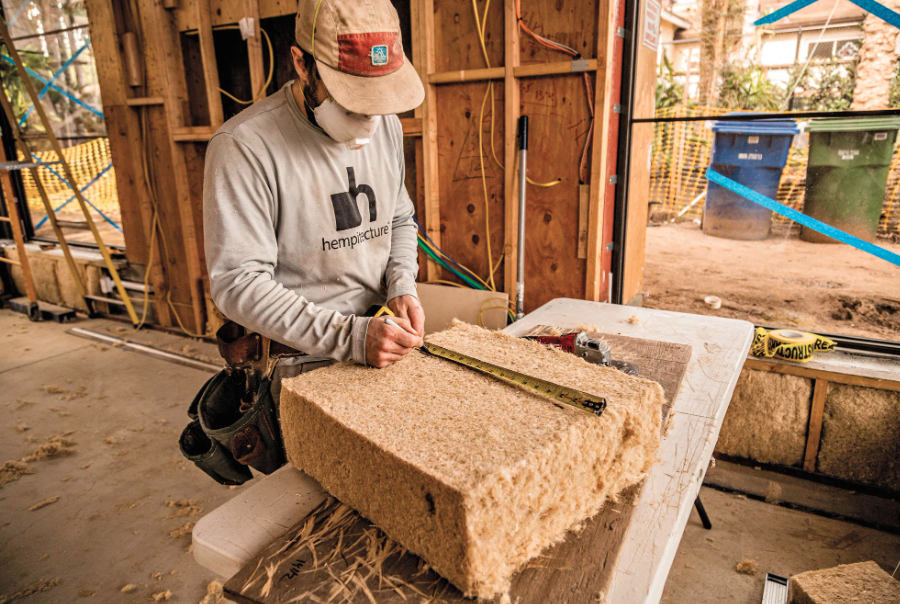
- Hempcrete for Building Insulation
You can build a house using hemp.
Hempcrete is a bio-composite material made from hemp fibers and lime.
This wonder material is manufactured by mixing the woody core of the hemp plant with a lime-based binder.
Its primary use on a construction site is as a filling material for single-layer walls.
Hempcrete is also perfect for insulation, with an R-value that ranges from 1.7 to 3.5 per inch.
Better heat insulation for homes means less heat loss and reduced energy consumption. Thus it is possible to save energy and reduce greenhouse gases with hemp.

- Hemp Transfers Carbon Underground
Hemp’s potential for carbon reduction extends from shoots to roots.
The plant reaches a height of 2 meters at maturity.
Its root system travels an equal length underground.
Reaching a depth of 2 meters, the roots break up compacted soil and leave behind carbon-rich organic matter.
It is estimated that hemp’s root system can contribute to the long-term storage of 8-15% of the plant’s total captured carbon in the soil.
- Hemp Reduces Agricultural Emissions
The production of synthetic fertilizers is a massive source of greenhouse gas emissions.
Traditional fertilizer production typically generates 4-6 kg of CO2 equivalent per kg of nitrogen fertilizer. Hemp requires about 60-90% less fertilizer than most similar crops, such as cotton.
Because it requires fewer fertilizers and pesticides, hemp agriculture has a slim carbon footprint.
- Hemp Replaces Carbon-Intensive Products
Hemp fibers can replace resource-intensive materials like conventional cotton textiles and plastics. Shifting from high-emission materials to carbon-negative materials for industries can significantly lower our carbon emissions. Large businesses that regularly purchase carbon credits can attain carbon reduction goals by switching to hemp alternatives.
Hemp products contribute to a more sustainable economy and reduce the reliance on fossil fuel-based products.
Hemp’s role in fighting climate change
The CO2 problem arises due to our industrial economy and over-reliance on petroleum and its byproducts.
Hemp helps with carbon reduction in two ways – reducing emissions and removing existing atmospheric CO2.
It can directly remove CO2 from the atmosphere and store it in its biomass.
Hemp also prevents further emissions by replacing materials like cotton textiles, concrete, and plastic.
Without a doubt, there are many environmental benefits of hemp cultivation. Supportive policies can encourage farmers to grow hemp for carbon reduction.
As we seek a solution to the climate change problem caused by too much carbon dioxide, hemp offers a rare combination of benefits. Increased adoption of hemp-based alternatives will help us mitigate the effects of climate change and, at the same time, build a sustainable future.
Vishal Vivek
Vishal Vivek is the Founder and CEO of Ukhi, a pioneering bio-materials company dedicated to ending plastic pollution by converting agricultural waste into high-performance compostable polymers. With a background in sustainable entrepreneurship and over a decade of technology experience, he leads Ukhi’s vision to create scalable, planet-positive material solutions. Previously, Vishal founded the Hemp Foundation, where he empowered more than 1,000 farmers and advanced sustainable livelihood initiatives. His work has been recognized through awards such as the HDFC Parivartan Grant and featured in leading publications like Forbes and Entrepreneur. Times Group recognized him as a legendary entrepreneur and published his biography in “I Did IT- Vol 2” alongside social pioneers like Bindeshwar Pathak (Sulabh International) and Anshu Gupta (Goonj). Vishal has authored more than 200 articles on sustainability and hemp, reflecting his deep expertise and advocacy for regenerative solutions. His commitment to grassroots impact led him to live in the remote mountains of Uttarakhand, where he immersed himself in the lives of marginal farmers, understanding their challenges and co-creating economic opportunities through hemp-based initiatives. A deeply passionate innovator, Vishal often draws inspiration from seemingly impossible achievements: “If Elon Musk can make rockets reusable, or Dashrath Manjhi can carve a path through a mountain with rudimentary tools, why can’t we eliminate the demon of single-use plastic while uplifting struggling farmers? We will make it happen—whatever it takes.” Ukhi is proud to be supported by premier institutions including IIT Guwahati, NSRCEL-IIM Bangalore, Indian School of Business (Hyderabad), Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR Pusa), and the Indian Institute of Packaging. Vishal is committed to demonstrating that business can be a powerful catalyst for global environmental and social good. Connect with Vishal Vivek
Related Posts
Top Five Reasons to Use Hemp in Home Decor
What is it that makes it have a soul and style of its own? Well, there’s love and family, and ot
A Miracle Drug: Can Hemp Cure Cancer?
Have you stumbled across this article while browsing the web for a research paper or as an ultimate
Top 10 Hemp Startups in the USA
While hemp startups in the USA seem rather contemporary, hemp has played an important role in the hi




